What is Co-Axial Cable?
Coaxial cable, also known as coax cable, is a type of electrical cable used to transmit high-frequency signals, such as cable television, internet, and radio signals. Coaxial cable consists of an inner conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, a metal shield, and an outer insulating jacket. The metal shield provides protection against electromagnetic interference and helps to maintain the integrity of the signal. Coaxial cable is preferred over other types of cable due to its ability to transmit high-frequency signals over long distances without significant signal loss. It is commonly used in homes and businesses for cable television, broadband internet, and other applications that require high-speed data transmission.
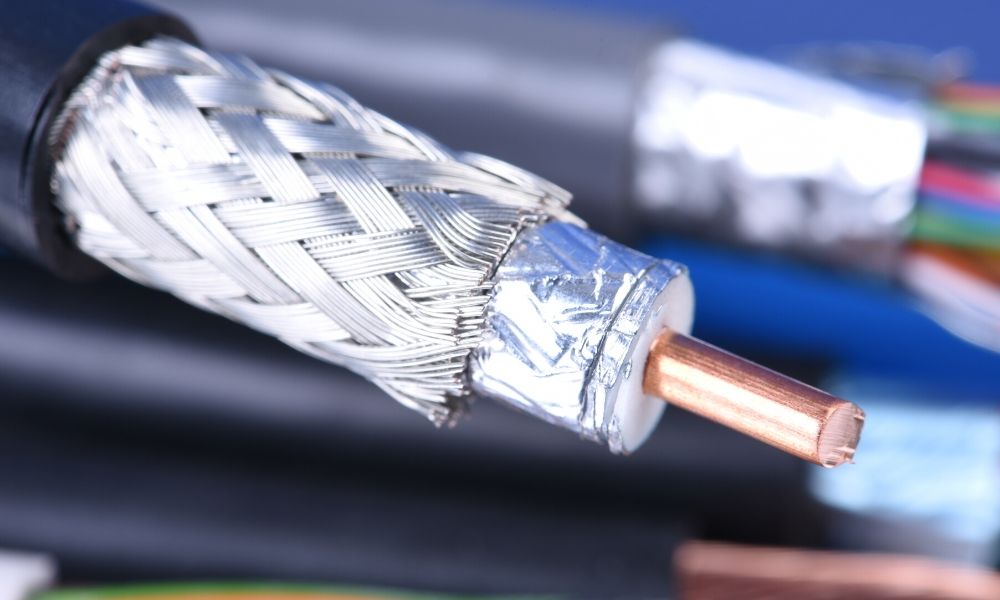
Structure of Co-Axial Cable:
The structure of a coaxial cable typically consists of the following components:
- Inner conductor: This is the central core of the cable and carries the electrical signal. It is usually made out of copper or aluminum.
- Insulating layer: This layer surrounds the inner conductor and serves to electrically isolate it from the other components of the cable. It is typically made of foam or solid polyethylene.
- Metal shield: This layer is a conductive shield that surrounds the insulating layer and helps to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting the signal. It is typically made of braided copper or aluminum.
- Outer jacket: This layer protects the cable from external damage and provides additional insulation. It is typically made of a durable, weather-resistant material, such as PVC.
- Braid: This is an optional component that can be added to the cable to provide additional protection against EMI.
Each of these components is carefully designed and selected to provide the best possible performance for the intended application. The structure of a coaxial cable is designed to minimize signal loss and interference, ensuring reliable and high-quality signal transmission over long distances.
Types of Co-Axial Cable:
There are several types of coaxial cables, including:
- RG-6: This is a common type of coaxial cable used for cable television and broadband internet. It has a relatively low signal loss and is suitable for use over long distances.
- RG-59: This type of coaxial cable is commonly used for older analog cable television systems and closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems. It has a lower bandwidth compared to RG-6 and is not typically used for high-speed data transmission.
- RG-11: This type of coaxial cable is similar to RG-6, but has a larger inner conductor and is designed for use over longer distances. It is commonly used for cable television distribution systems.
- Tri-Shield: This type of coaxial cable has three layers of shielding, providing superior protection against EMI. It is commonly used for cable television and broadband internet in areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference.
- Dual Shield: This type of coaxial cable has two layers of shielding, providing good protection against EMI. It is commonly used for cable television and broadband internet in residential and small commercial applications.
- Hardline: This type of coaxial cable is made from a solid outer conductor and is used for high-power, long-distance applications, such as broadcast television and radio transmission.
The type of coaxial cable you choose will depend on your specific needs, including the type of signal you are transmitting, the distance the signal must travel, and the level of protection against EMI that you require.
Where to use coaxial cable?
Coaxial cable is commonly used in the following applications:
- Cable television: Coaxial cable is used to distribute cable television signals from the service provider to homes and businesses.
- Broadband internet: Coaxial cable is used to transmit high-speed internet signals from the service provider to homes and businesses.
- Radio frequency (RF) transmission: Coaxial cable is used to transmit RF signals for radio and television broadcasting, satellite communications, and other applications.
- Closed-circuit television (CCTV): Coaxial cable is used to transmit video signals from security cameras to a central monitoring station.
- Medical equipment: Coaxial cable is used to transmit high-frequency signals in medical equipment, such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners.
- Aerospace and military: Coaxial cable is used in aircraft, spacecraft, and military applications to transmit high-frequency signals.
- Automotive: Coaxial cable is used in vehicles to transmit audio and video signals, as well as control signals for various systems.
Coaxial cable is a versatile and reliable transmission medium that is widely used in a variety of applications due to its ability to transmit high-frequency signals over long distances without significant signal loss.
Advantages of coaxial cable:
The following are some of the advantages of coaxial cable:
- High bandwidth: Coaxial cable has a high bandwidth, which allows it to transmit high-frequency signals with minimal signal loss. This makes it ideal for applications that require high-speed data transmission, such as broadband internet and cable television.
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection: Coaxial cable has a metal shield that helps to prevent EMI from affecting the signal. This makes it ideal for use in areas with high levels of EMI, such as industrial and urban environments.
- Durability: Coaxial cable has a tough outer jacket that protects it from damage and provides additional insulation. This makes it ideal for use in applications that require a durable cable, such as outdoor installations and harsh industrial environments.
- Versatility: Coaxial cable is available in a wide range of sizes and configurations, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from cable television and broadband internet to medical equipment and aerospace applications.
- Easy to install: Coaxial cable is relatively easy to install, and can be terminated using standard connectors. This makes it ideal for use in DIY and professional installations.
- Reliability: Coaxial cable is a reliable transmission medium that is widely used in a variety of applications. Its high bandwidth and EMI protection make it ideal for use in demanding applications where reliable signal transmission is essential.
Overall, coaxial cable is a versatile and reliable transmission medium that offers many advantages, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Disadvantages of coaxial cable:
Below are some of the disadvantages of coaxial cable:
- Cost: Coaxial cable is typically more expensive than other types of cable, such as twisted pair and fiber optic cable. This can make it a more costly option for large installations.
- Heavy and stiff: Coaxial cable is often heavy and stiff, which can make it difficult to install and handle. This can be a disadvantage in applications where the cable needs to be run through tight spaces or around corners.
- Limited flexibility: Coaxial cable is limited in terms of its flexibility, which can make it difficult to route the cable through tight spaces and around obstacles.
- Signal loss over distance: Coaxial cable can experience signal loss over long distances, which can affect the quality of the signal. This is especially true for high-frequency signals, which can be affected by cable length and cable quality.
- Susceptible to damage: Coaxial cable can be susceptible to damage, especially when exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical damage.
- Limited applications: Coaxial cable is primarily used for transmitting high-frequency signals, such as RF signals, video and audio signals, and high-speed data. It may not be suitable for applications that require a different type of cable, such as fiber optic or twisted pair cable.
Overall, while coaxial cable offers many advantages, it also has some disadvantages, such as cost, stiffness, signal loss over distance, and susceptibility to damage. These factors should be considered when choosing a cable for a particular application.
Conclusion:
Coaxial cable is a widely used transmission medium that offers many advantages, such as high bandwidth, EMI protection, durability, versatility, easy installation, and reliability. However, it also has some disadvantages, such as cost, weight and stiffness, limited flexibility, signal loss over distance, susceptibility to damage, and limited applications. When choosing a cable, it’s important to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each type of cable to make an informed decision.
